Topics Map > Canvas > External Applications
Canvas (Accessibility) - Using the UDOIT Cloud Accessibility Tool
The Universities of Wisconsin has upgraded to UDOIT Advantage. Instructors can now scan uploaded files for accessibility. Just click the "Review Course Files" link to quickly and easily analyze, remediate and replace documents.
For an overview of the tool, see the UDOIT Cloud Accessibility Tool website.
Note: At this time, only instructors can generate alternate document formats, students do not have this ability.
Contents
Should I Use UDOIT or the Canvas Accessibility Checker?
The UDOIT Cloud Accessibility Tool is designed to compliment Canvas's native Accessibility Checker, and can be used in combination with it. Each tool has its own particular strengths.
Canvas Accessibility Checker
- Scans content within the Rich Content Editor
- Scans one page at a time
- Looks for 11 accessibility issues
UDOIT
- Scans published and unpublished html content
- Scans published files
- Scans entire course at one time
- Looks for 21 accessibility issues
Finding Accessibility Issues
As an instructor, you can follow these steps to find potential accessibility errors and suggestions in your Canvas courses:
- Log in to Canvas at https://uws.instructure.com or from your institution's custom URL.
- Use Canvas's Dashboard or Courses page to navigate to any course where you have the Teacher role.
- In the course navigation menu on the left, select Course accessibility checker (UDOIT). Only users with a Teacher or Administrator role will see this link in the course navigation.
- You may get a prompt indicating "Cidi Labs UDOIT Cloud is requesting access to your account." Click Authorize.
- UDOIT will automatically scan your course (which may take a minute or two) and display a scorecard indicating an overall Accessibility Score
NOTE: For information on how scores are calculated please click the informational icons within the UDOIT interface or review Canvas - UDOIT Advantage Course Accessibility Scoring Criteria .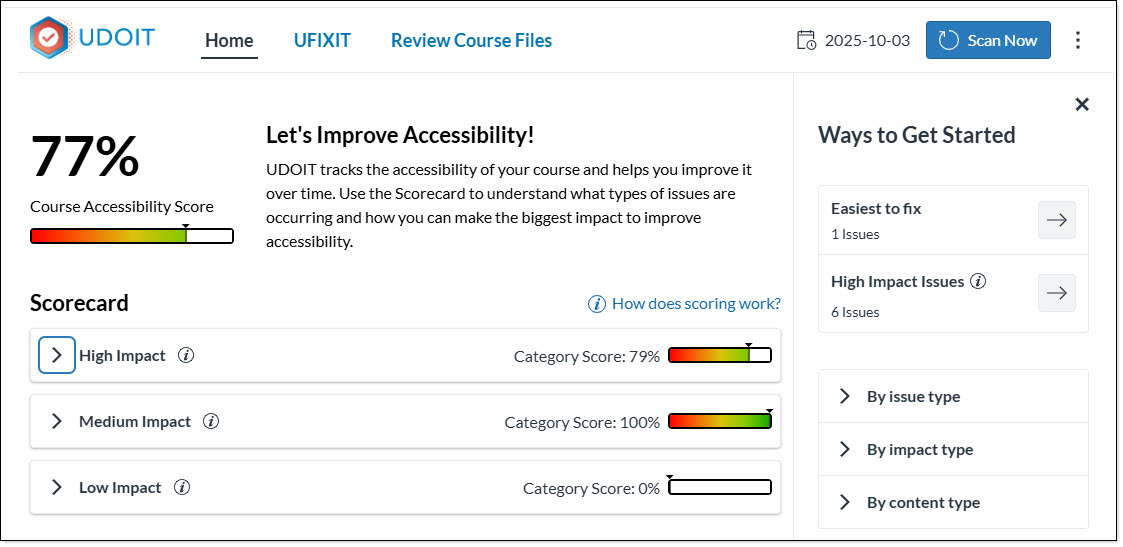
- Begin reviewing errors and suggestions in one of the following ways.
NOTE: Errors are issues which MUST be fixed to ensure equal access. Suggestions are issues which SHOULD be fixed to ensure equal access.- Ways to Get Started: (panel on right of screen) displays a subset of the Errors and Suggestions for the course.
- UFIXIT (located towards the top of the page) focuses on text written in pages, announcements and other areas of Canvas
- Review Course Files (located towards the top of the page) to see errors associated with uploaded items.
Resolving Accessibility Issues
UDOIT makes it easy to fix most Canvas course accessibility issues from a single page.
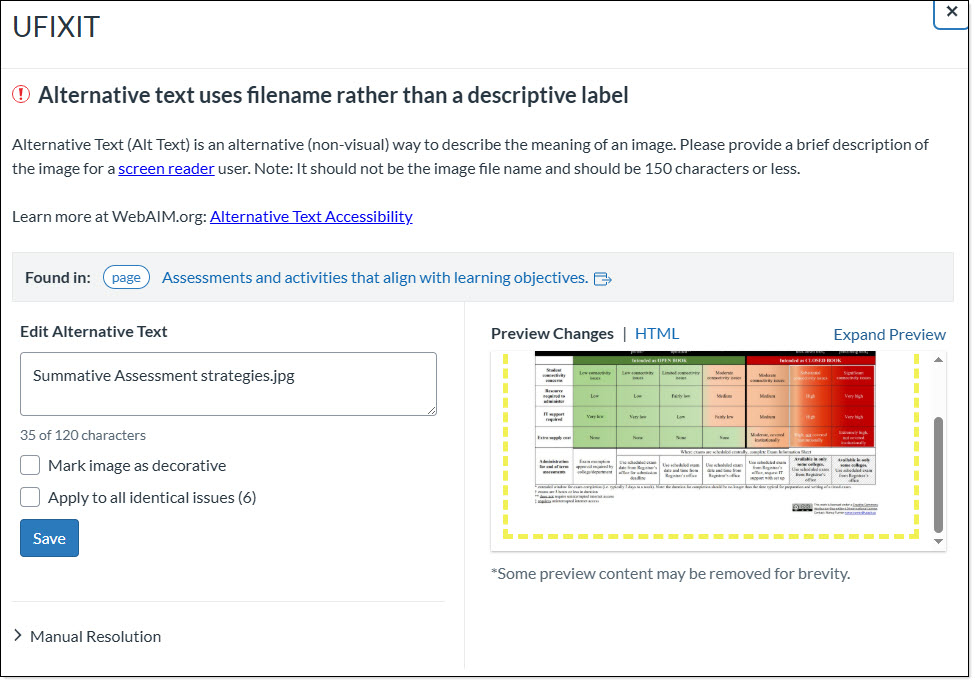
Clicking on an Error or Suggestion will bring up a page with a description of the issue, a preview of where it appears in the course, and a text entry box or menu to fix the issue. Follow the prompts on the screen to resolve the issue (usually by entering new text or selecting a choice from a menu).
In this example, the alternative text provided for an image repeats the filename of the image instead of giving a full description. UDOIT has provided a description of why this is an issue, and a preview of the image in question (in this case, it is an image of a chart). UDOIT provides a text entry box titled "Edit Alternative Text" to allow the instructor to directly fix the issue.
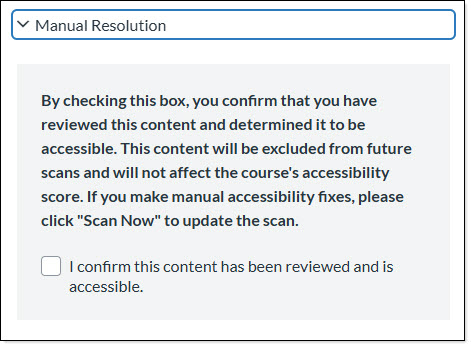
UDOIT also provides a "Manual Resolution" checkbox to indicate when an issue has been resolved outside of UDOIT.
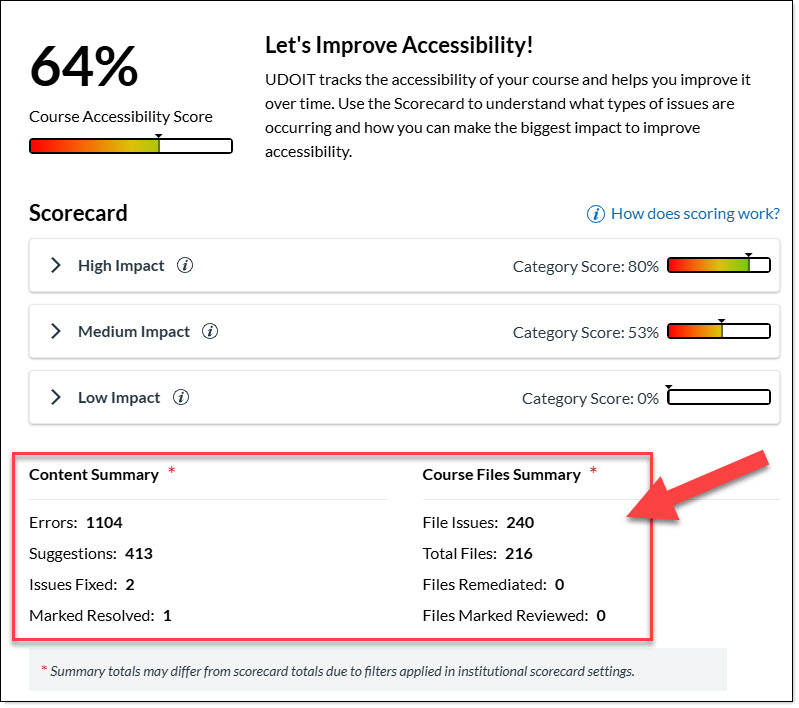
As you fix or manually resolve issues and review files in the course, the UDOIT Home page tracks your progress. It lists how many "Issue Fixed," "Manually Resolved," and "Files Reviewed" you have, and it updates the number of remaining Errors and Suggestions.
SpeedFixit
SpeedFixit is a feature that will assist in resolving accessibility Issues for images and color contrast. It will automatically provide suggestions for issues all you need to do is approve. For more information and specific instructions, please see the SpeedFixit support materials.
Continue fixing or manually resolving issues until your course has reached the desired level of accessibility.
Tips for Common Errors
Links should contain text
Because many users of screen readers use links to navigate the page, providing links with no text (or with images that have empty "alt" attributes and no other readable text) hinders these users. Please add descriptive text.
Base font tag should not be used.
The basefont tag is deprecated and should not be used. Investigate using stylesheets instead.
Blink tag should not be used.
The blink tag should not be used. Ever.
Insufficient text color contrast with the background.
Text color should be easily viewable and should not be the only indicator of meaning or function. Color balance should have at least a 4.5:1 ratio for small text and 3:1 for large text. Warning: using UDOIT to fix one section of text may invalidate the contrast in nested sections of text that are not the same color.
Avoid using color alone for emphasis.
When emphasizing text, you may use color with sufficient contrast as long as you also apply some other form of emphasis, such as bold or italics. This ensures that screen reader users are aware of the text's importance.
Document reading direction.
Changes in text direction in inline content should be indicated using any HTML element (for example, span) with a 'dir' attribute indicating left-to-right or right-to-left. For example, a Hebrew phrase within an English paragraph should have its own text direction indicated.
All ‘embed’ elements must have an associated ‘noembed’ element.
Because some users cannot use the embed element, provide alternative content in a noembed element.
Font tag should not be used.
The font tag is deprecated and should not be used. Investigate using stylesheets instead.
Headings should contain text.
No alternative text found
Alternative text (alt text) is an alternative (non-visual) way to describe the meaning of an image. Please provide a brief description of the image for a screen reader user. Note: alt text should be more than image file name.
Learn more at WebAIM.org: Alt Text Accessibility
Alternative Text should not be the image filename
Alternative text (alt text) is an alternative (non-visual) way to describe the meaning of an image. Simply repeating the image file name is not descriptive enough. Please provide a description.
Learn more at WebAIM.org: Alt Text Accessibility
Alternative Text is more than the maximum allowed characters
Alternative text (alt text) is an alternative (non-visual) way to describe the meaning of an image. Although alt text should be descriptive, it should also be short, typically no longer than 80-125 characters. Note: For the UW Digital Learning Environment, this limit is set to 120 characters to align with the Accessibility Checker in the Canvas Rich Content Editor.
Learn more at WebAIM.org: Alt Text Accessibility
Alt text for images within links should not be empty.
Alternative Text (Alt Text) is an alternative (non-visual) way to describe the meaning of an image. Please provide a brief description of the image for a screen reader user. Note: It should not be the image file name.
Learn more at WebAIM.org: Alt Text Accessibility
Images should not have a placeholder as alternative text.
Image elements should have an “alt” attribute.
Decorative images should have empty alternative text.
Image description is too long.
Marquee tag should not be used.
No table headers found.
No row or column scopes declarations found in table headers.
Closed captions do not match course language.
- If the video is in Kaltura, you can add and edit captions.
- Contact the creator of the video and request captions in your course language be added.
- Create captions yourself using a service like Amara (http://amara.org/).
- Find a different video that has closed captioning for your course language.
Closed captions cannot be checked
Multimedia objects should have a text equivalent
- If the video is in Kaltura, add captions and edit them to improve accuracy
- Contact the creator of the video and request captions in your course language be added.
- Create captions yourself using a service like Amara (http://amara.org/).
- Find a different video that has closed captioning.
No closed captions found.
Closed captions were auto-generated.
Connection to the Kaltura Service Failed
This issue does not prevent video playback—it’s just a limitation in UDOIT’s validation process. UDOIT (Universal Design Online Inspection Tool) cannot directly verify Kaltura video playback due to security constraints. The necessary API token would violate UW system security policies. If you encounter this issue in a UDOIT report, the solution would be to manually check Kaltura videos or set their publishing status to “Public”.

